Speech Therapy
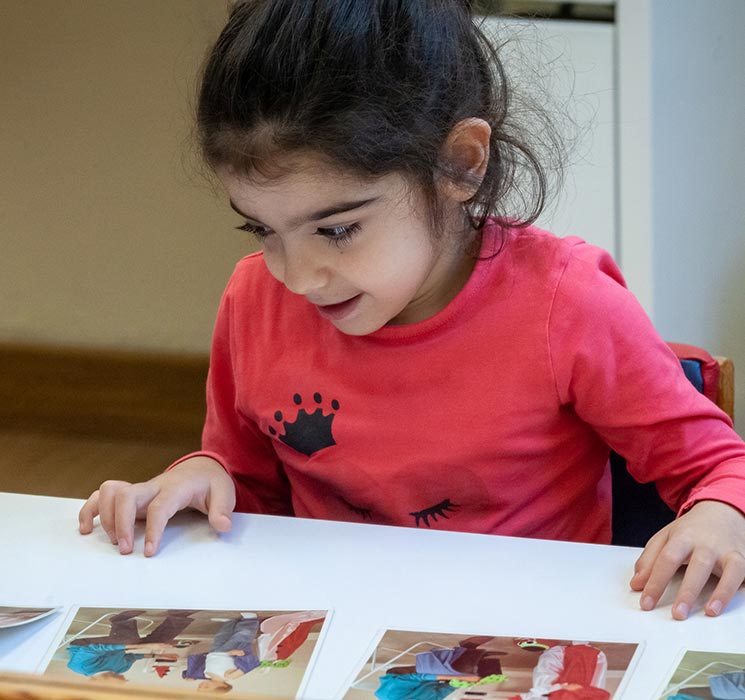

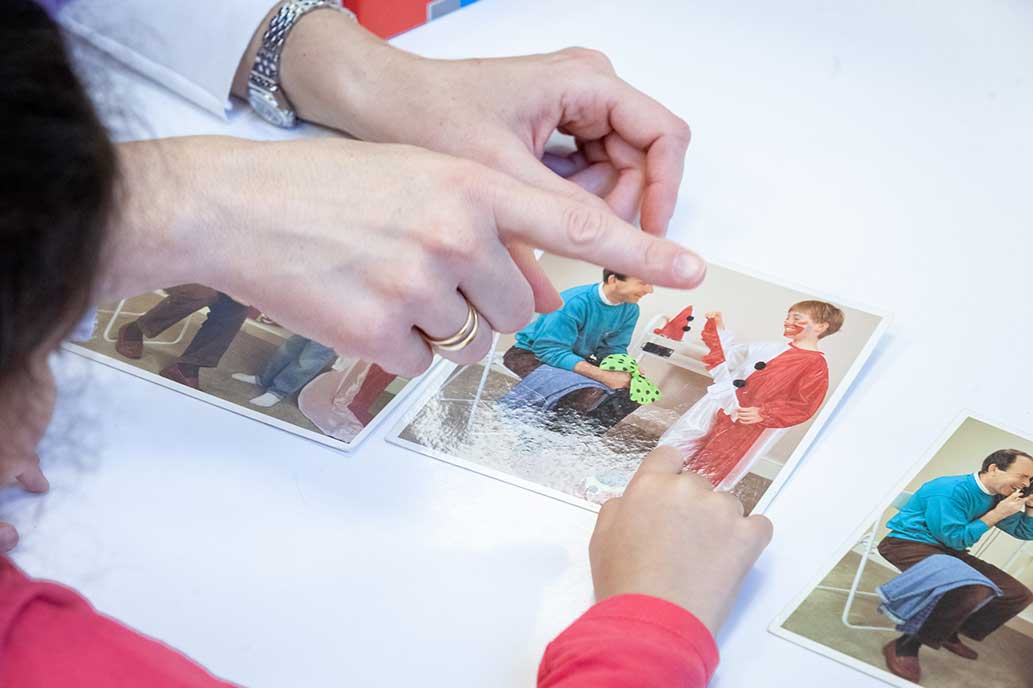
The Speech Therapy department deals with speech and language disorders as well as with eating difficulties in infants, pre-school and school-age children.
Each child is treated in an integrated manner that increases the function of eating and communication. Speech therapists:
- Assess the child’s level of communication and diagnose any speech and language disorders
- Assess eating difficulties
- Deal with eating difficulties and speech disorders at an early stage with individual therapy interventions and innovative programs.
The Speech Therapy program is modelled on the Early Intervention principles of the WHO-endorsed International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF).

The Early Speech Therapy Intervention involves both the infants’ families and the other members of the interdisciplinary group. The REEL Scale is also used for the infants. Information and guidance to parents along with a harmonious therapist- child-parent relationship helps the implementing the therapy instructions at home. The Intervention involves:
- Prevention: Potential risk factors are taken into account (e.g. long stay at the NICU, history of non-oral feeding, breast-feeding difficulty, limited interest in interaction, limited pre-verbal communication etc.) in order to apply techniques that prevent or mitigate possible more serious difficulties in the infant’s feeding and/or communication if possible.
- Assessment: A detailed history of the parents taken with sensitivity, observation of the infant during its interaction with people and with the surroundings and/or during feeding time, as well as the use of ICF-based assessment protocols, help describe the infant’s potential and needs. This helps establish the necessity and the form of the intervention.
- Therapeutic intervention:
Objectives:
- adequate and safe feeding of the infant consistent, to the extent possible, with the developmental milestones. The timely intervention to deal with feeding difficulties concerns infants with physical, sensorial and/or behavioral causes (e.g. pathological reflexes, breastfeeding difficulty etc.)
- enhance the infant’s communication abilities for a more effective and functional communication with the family members and its interaction with the surroundings.
Forms of intervention:
- Support and train the parents to identify their child’s potential and difficulties and apply the required therapeutic techniques in their daily practice.
- Individual regular or periodic therapy sessions
- Participation in the Interdisciplinary Group
The objective is exchange of information, problem solving, a holistic approach to the needs of infant and family as well as to jointly set the objectives and make decisions about the therapy plan.
- Coordination on issues of feeding and swallowing
Communication with all the medical and therapeutic specialists involved, referral for imaging tests whenever necessary (e.g. gastroscopy, chest x-ray, endoscopy (FEES), VFSS etc.), referral to a Clinical Nutritionist and decision making with the treating doctors about the best possible feeding method (oral or alternative).
- Transition Support
Ensures the smooth transition to a new program or framework whenever necessary, such as formal education, outside therapy program, family moving elsewhere.
- Scientific work
The Speech Therapy group participates in scientific work, presents papers in conferences, organizes training of the ELEPAP staff and creates assessment and therapeutic protocols.
- Assessment and Therapeutic intervention
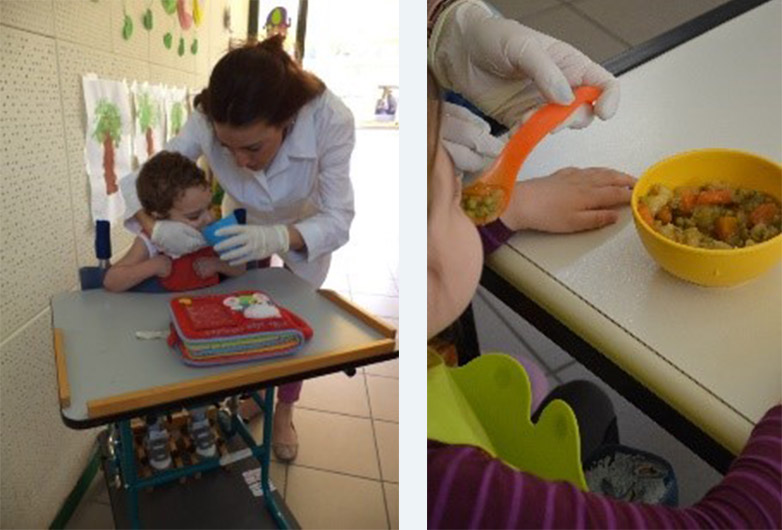
The early assessment and treatment of chewing-swallowing difficulties which have physical (e.g. cerebral palsy) or non-physical causes (e.g. behaviour) is important for the adequate and safe feeding of the child as well as for improving the family’s quality of life. Speech therapists specialized in dysphagia make the assessment and intervention and train the parents.
- Medical follow up of the children
The dysphagia program is staffed with medical specialists (Physiatrist specialized in child rehabilitation, Child Gastroenterologist, Child Pneumonologist) and Clinical Dietician. They cooperate with the Speech Therapist and with the parents to deal with each child’s specific difficulties. The child is referred to the specialists depending on the type of need (e.g. breathing problems, constipation, reflux, low weight, etc.).
- Dysphagia Team
This is an interdisciplinary team set up to deal with serious eating difficulties using an innovative approach that takes into account the child’s and the family’s needs and wishes. After a medical examination and discussion between the specialists (medical doctors, therapists, dietician, psychologist) and the parents, different ways of dealing with the difficulties are proposed.
Every day the speech therapists cooperate with occupational therapists and physiotherapists in order to teach the children to eat.

Children with motor and developmental disorders (e.g. cerebral palsy, syndromes) may have difficulties in communication such as speech and/or language retardation, articulation disorders, phonological disorders, verbal dyspraxia, dysarthria, fluency disorders.
The department’s expert speech therapists perform speech and/or language assessments in order to determine the potential and the needs of each child and to set the therapy goals in cooperation with the parents.
The therapeutic intervention may take place individually, in a group, it can even be intertherapeutic, with parallel parent support and education. Parent education relates to explaining the child’s abilities and difficulties and the application of different techniques. Moreover, external experts and bodies are involved in order to facilitate the child’s communication in different settings.